International Mentoring Programme and Training Courses
The share of women in the Czech parliament has languished at around one in five, while their share of the Czech seats in the European Parliament is under one in four. The NGO Fórum 50% decided to do something about this by launching projects to raise the level of women’s political representation.
One of them is a mentoring scheme, which partners Czech female politicians with Danish and Norwegian women who have successful political careers and valuable experience to share. The mentoring involved face to face meetings and regular contact by e-mail and Skype.
Fórum 50% also organised two short courses for 15 female candidates in the 2014 European Parliament elections. These comprised media training, individual coaching, a weekend seminar and a debate with a sitting MEP.
Helping women to win
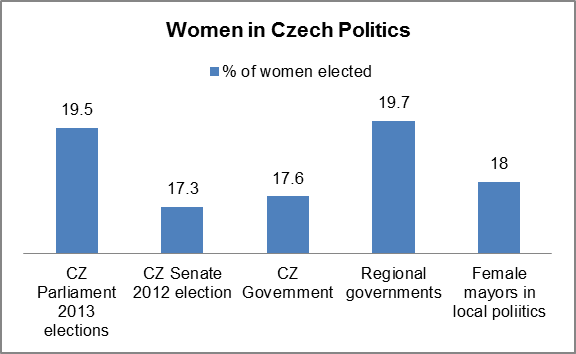
Czech women are still under-represented in political decision-making, and make up a little less than 20% of the national legislature. Similar or even lower figures reflect women’s involvement at regional and local level. This is considerably lower than in the majority of the EU Member States. The gender imbalance in political decision-making, which is a long-term issue in the Czech Republic, results from political parties placing women in unwinnable positions on candidate lists. Nor do the parties provide tools to support or promote women politicians, and there are no mentoring programmes or courses to help women develop their soft skills.
The NGO Fórum 50% decided to fill this gap by launching, in collaboration with The Nordic Chamber, an international mentoring and training programme for female candidates in the Czech Republic. Fórum 50% is a non-profit organisation founded in 2004 which supports the equal participation of women and men in politics and decision-making. It strives for a more balanced decision-making process which takes both sexes’ views and life experience into account. It encourages women to become politically active, supports female politicians and leaders, and works with political parties and other bodies on concrete measures. Its guiding principle is to be non-partisan. Its main activities are:assessing political parties’ ballots and agendas from the gender point of view, running a ‘Women-Friendly Party’ competition, workshops, trainings and consultancy;conducting opinion polls on the representation of women in Czech politics;training women politicians and women interested in politics, networking and mentoring;media campaigns to support women politicians in the elections (public discussions, press conferences, workshops, web site, conferences);studies on women's representation, in cooperation with number of research institutes co-operation with other NGOs in the Czech Women's Lobby.It is funded by the European Commission and EEA grants.
Seeing mentoring as a successful tool, the Czech NGO drew inspiration from Denmark and Norway, where political parties run mentoring programmes and training courses for female politicians. It thereby relied on the methodology of the Danish Centre for Gender, Equality and Ethnicity (KVINFO) which already for more than a decade has been at the forefront of developing mentoring initiatives for women politicians in Denmark and has established a broad Mentoring Network. The successful Nordic mentoring initiatives had already inspired the European Women’s Lobby when they launched in 2013 the first European Political Mentoring Network within the framework of their 50/50 Campaign in order to address the lack of gender parity and ethnic diversity in political decision-making at European level.
Mentoring on the Nordic model
Fórum 50%’s international mentoring programme aims to increase women’s representation in Czech politics by sharing experiences from countries where it is already at a high level. The mentors are female politicians from Denmark and Norway with long-term experience who influenced the political scene in their home countries. They are not chosen due to their political party views, but their personal engagement, interest and skills.
There are now ten mentoring pairs who meet face to face and stay in touch at least twice a month through e-mail and Skype. Both mentors and mentees come from a range of different political parties and different levels of politics. The Nordic mentors were chosen on the basis of their knowledge and experience, while for the Czech mentees there were two qualifications: they had to already be involved in politics at local, regional or national level and they had to be committed to gender equality. Mentors and mentees were matched on the basis of shared political interests and whether the mentors’ skills fitted the mentees’ needs. Once the mentees had defined the specific goals they wanted to work towards in the mentoring process, the mentors gave them feedback and shared their experience.
They have focused on different topics, including promoting gender equality, negotiating within political parties, campaigning, and challenges in becoming an MP, balancing political and private life, and responding to sexist statements.
The programme lasts 18 months for each mentee and consists of three 6-month blocks with a specific political topic chosen for each block (e.g. efficiency and transparency of public administration, social and educational policies for children and elderly, immigration issues, employment policy, etc.). These topics are discussed not only at the closed meetings between mentor and mentee but also at the seminars open for other Czech politicians. The mentoring programme also foresees the visits of mentees to the mentors’ country and the establishment of a communication platform to exchange and share views.
The mentoring programme is part of a broader project called Equilibrium between Women and Men, which started in July 2014 and will run until April 2016. It is financed by the Norway Grants fund, and its partners are the Danish Embassy in Prague and the Nordic Chamber of Commerce in the Czech Republic.
Training for prospective MEPs
In February and March 2014, Fórum 50% also ran training courses for 15 female candidates in the 2014 European Parliament elections. The aim was to support candidates from different political parties through training activities such as a workshop on how the European Parliament works, courses on negotiation and media skills, and individual coaching. Selection of trainees was based on two criteria: a clear vision of future work in the parliament and support for gender equality.
The courses comprised three hours of media training, three hours of individual coaching and a weekend seminar, and were delivered by internal and external lecturers and coaches from the International Coach Federation. Trainees also took part in a discussion with Czech female MEP Zuzana Brzobohatá. This training was part of a larger international project supported by the European Commission called More Women in European Politics, More Women in 2014.
Women’s representation improves
The mentoring is successful because the nature of the mentoring relationship is carefully thought through before the start. What the mentee and mentor are to focus on during the mentoring process is set out in a mentoring agreement and a clear activity plan. Further success factor are the enthusiasm and dedication of all the participants who work hard to reach the set goals in spite of their busy agendas as politicians. Mentors and mentees see the programme as a mutually rewarding process which enables them to expand their political networks, share experiences and perspectives, gain fresh ideas and get to know different political systems. The programme benefits from sharing of international experience and knowledge coming from countries where women’s political representation is high.
The European Parliament candidates found the training especially valuable, as it taught them new soft skills and enabled them to network with other Czech female politicians. It is difficult to say whether the programmes had any direct impact on the outcomes of the elections. However it is true that recent years have seen certain improvement in women’s participation particularly in the European Parliament elections. Compared to 2009 the 2014 elections demonstrated some increase in the proportion of elected female MEP: from 18,2% to 23,8%.
Contacts
Markéta Mottlová | Halka Jaklová
Coordinators of mentoring programme
Fórum 50% | Plzeňská 846/66 | Praha 150 00 | Czech Republic
Jana Smiggels Kavková
Director Fórum 50% | Coordinator of training courses
Fórum 50% | Plzeňská 846/66 | Praha 150 00 | Czech Republic
Further information
NB image copyright
Image from Fórum 50% website.
More on good practices
Downloads
-
Czech female politicians learn from international experience - Czech Republic
- Language
- EN
- File type and size
- PDF, 1.07 MB